Includes the concepts of:
- speed
- velocity
- acceleration
- time
- distance
- displacement
Vectors: is a quantity which express both magnitude and direction.
- magnitude is how big or how small a number is
- direction is which way something is headed or directed.
- example; velocity, displacement, force, accerleration
Scalars: is a quantity which express magnitude only
- no direction is specified
- example; speed, mass, distance, energy
Distance: how far something has traveled
- no direction is specified
- commonly measure in meters, kilometers, and centimeters
- is a scalar
Displacement: how far something is from its starting point
- direction is specified
- is a vector
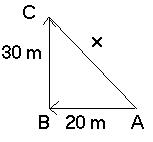
Example: An object travel 20 meters west then 30 meters north.
b) What is the displacement?
Use Pythagorean Theorem: a^2 +b^2 = c^2
a) Distance = 20 m +30 m = 50 m
b) Displacement = 20^2 +30^2 = x^2
√ (1300) = x^2
36.06 m = x (North West)
Speed: how fast something is traveling
- speed is the distance covered in a given amount of time
- is a scalar
Example 1) An object covered a distance of 75 kilometers in half an hour. What is the speed in a) kilometers/hour b) meters/second
a) s = d/t = 75 kilometers / .5 h = 150 km/h
b) (150 km)/ h * (1000 m)/ km * h/(3600 s) = 41.67 m/s
Example 2) An object covered 450 m in 20 s. What is it speed in a) m/s b) km/h?
a) s= d/t = 450 m/20 s = 22.5 m/s
b) (22.5 m)/ s * km/ (1000 m) (3600 s)/h) = 81 km/h
Example 3) A rifle fire a bullet at a target. The speed of the bullet is 700 m/s. The target is located 250 meters away.
a) How long does it take for the bullet to hit the target?
b) What is the bullet speed in km/h?
a) s = d/t => 700 m/s = (250 m)/ t => 250 m*(1s/700 m) = (t/250m) *250 m => 250/700 = t, t = .35 secs.
b) (700 m)/ s * (3600 s)/h * km/ (1000 m) = 2520 km/h
Velocity: how fast something is traveling and in what direction
- is a vector
Example:
a) An object travel 45 m/s is a speed
b) An object travel 45 ms due south is a velocity
Acceleration: how fast speed or velocity changes
- the rate at which speed or velocity changes
- if an object speed up, it has a positive acceleration
- if an object slowing down, it has a negative acceleration
The formula to calculate the acceleration is: a = Δ's / t
- Δ's is the change in speed, Δ is Delta
- t is the time
- the change in speed is calculate using sf - si
- sf = the final speed
- si = the initial speed
- therefore a= (sf - si)/ t
Examples 1) A new Nissan GT-R 35, Spec V acceleration from 0 mph to 60 mph in 3.2 secs. What is it rate of acceleration?
a = (sf - si) /t = (60 - 0) / 3.2 = 18.75 (m/h)/s, mph = miles per hour. So in 1 sec, the car go 18.75 miles per hour.
Example 2) A car goes from 20 m/s to 50 m/s in 10 s. What is the rate of acceleration?
a = (sf - si) /t = (50-20)/ 10 = 3 m/s^2
(m/s) /s => m/s x 1/s = m/s^2
The average speed of a uniformly acceleration object:
Example: If a car goes from 10 m/s to 30 m/s in 3 s.
a) What is its acceleration rate?
a = (sf - si)/t = (30 - 10) / 3 = 6.67 m/s^2
b) What is it average speed over the 3 s interval?
-
The formula to calculate average speed: s = (si + sf) /2
= (10 + 30) / 2 = 40/2 = 20 m/s
Rearranging acceleration formula: a = (sf - si) /t
- First multiply both side by t => a*t = sf - si
- Final speed of an object base on initial speed, acceleration and time. => sf = si +a*t
Example 1) An airplane traveling at 300 m/s accelerates uniformly at the rate of 12 m/s^2. What its speed be at the end of 30 secs?
si = 3000 m/s a = 120 m/s^2 t = 30 s sf = ?
sf = si + at = 300 m/s + (120 m/s^2) (30 s)
= 300 m/s + 360 m/s = 660 m/s
Example 2) An automobile accelerate at the rate of 7.5 m/s^2. It goes from 15 m/s to 85 m/s. While it is accelerating, how long did it take to reach 85 m/s ?
a = 7.5 m/s^2 si = 15 m/s sf = 85 m/s t = ?
sf = si + at => 85 m/s = 15 m/s + (7.5 m/s^2) t
70 = 7.5 t, t =9.33 s
Distance based on si, a, and t: To calculate how far
an object travels
based on initial speed, acceleration rate, and time.
The following equation is used => d = si*t + (1/2) a t^2
- d = distance traveled
- si = initial speed
- a = acceleration rate
- t = time
Example 1) A rocket is accelerate from 300 m/s at
the rate of 9.5 m/s^2 for 20 sec.
a)What is the rocket final speed?
si = 300 m/s a = 9.5 m/s^2 t = 20s
sf = si + at = 300 m/s + 9.5 m/s^2 (20s)
= 300 m/s + 190 m/s = 490 m/s
b) What is the distance traveled by the rocket during the 20 sec?
d = si*t + (1/2) a t^2 = 300 m/s (20s) = (1/2)(9.5 m/s^2)(20s)^2
= 6000 m + 1900 m = 7900 m
Example 2) A rock is dropped off a bridge. Gravity
accelerates falling objects at the rate of 9.8 m/s^2.
a) If the rock fall for 5 sec, how far did it traveled?
si = 0 a = 9.8 m/s^2 t= 5s
d = (0) (5s) + (1/2)(9.8 m/s^2) (5s)^2
= 0 + (9.8 x 25)/2 = 122.5 m
b) How fast was it going at the end of 5 secs?
sf = si + at = 0 + (9.8 m/s^2) 5s = 49 m/s
The last kinematics formula:
a = (sf^2 - si^2) / 2d d = (sf^2 - si^2) / 2a
- sf = final speed
- si = initial speed
- d = distance traveled
- a = acceleration rate
Example 1) A supersonic jet travelling at 400 m/s accelerate to 750 m/s at a rate of 18 m/s^2. What distance does it cover during this time?
si = 400 m/s sf = 750 m/s a = 18 m/s^2
d = [(750 m/s) ^2 - (400 m/s)^2] / 2 (18 m/s^2) = 11, 180.55 m
Example 2) A race car travels 800 m while acceleration at the rate of 5 m/s^2. If its initials speed was 30 m/s. What was it final speed?
sf = si + at a = (sf^2 - si^2)/ 2d
5 m/s^2 = [sf^2 - (30 m/s)^2 ] / 2 (800 m)
1600 (5) = [(sf^2 - 900)/ 1600] (1600)
8000 + 900 = sf^2 -900 +900
8900 = sf^2
√8900 = sf^2
94.34 m/s = sf


No comments:
Post a Comment